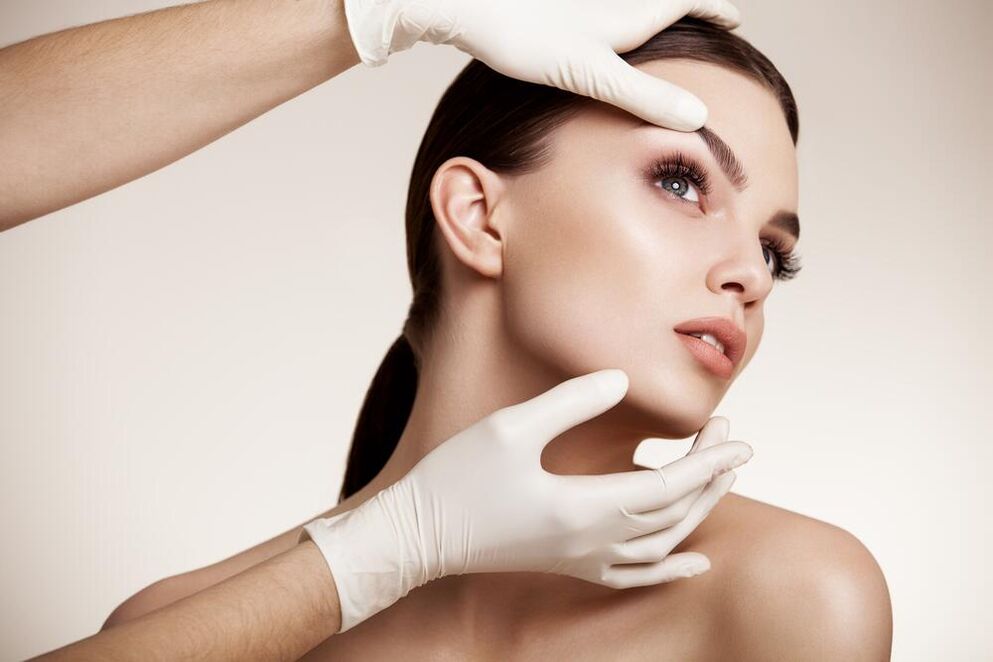
In aesthetic medicine, there are several different methods of facial rejuvenation: ablative fractional laser, fractional radiofrequency with microneedles, smart lifting, L-polylactic acid, hyaluronic acid. What to choose? Which rejuvenation option is really better?
Which method is best?
None of these methods can be called the best. Each of them uses different mechanisms, suitable for different skin types and skin problems, face shape, age, degree of skin damage and facial tissue atrophy, and also involve different recovery times after treatment. Each of them has its own pros and cons.
By comparing rejuvenating procedures, the patient understands what an individual approach entails. There is no universal method. Therefore, the ideal solution for people seeking help from an aesthetic clinic is to go somewhere where there are many therapeutic options. The wider the range of possibilities, the better it is to individualize the offer.
Fractional laser
Let's start with fractional ablation laser because it is the most common method. And from an efficiency point of view, an ablative laser is the only correct option.
Fractional laser before and after
Ablative fractional laser comprehensively tightens and rejuvenates the skin. It acts in two directions:
- On the surface of the skin, promoting its active refreshment - the skin becomes smooth, beautiful, pleasant to the touch, has an even color;
- Stimulates collagen production, which leads to a lifting and thickening effect.
Ablative fractional laser is well suited for rejuvenating aging skin: gray, flabby, with signs of photoaging and wrinkles. It is worth using this method both for preventive purposes (30+) and in old age, when the problems of aging skin are already clearly visible.
However, even such a perfect device is not a solution for everyone.
- First of all, the skin after the procedure requires several days of staying at home, and not all patients can afford a long recovery period.
- Secondly, if the skin is sagging and thin, then the laser will not give the desired effect. It will not be possible to sufficiently restore tissue volume with its help, and we will not have such a deep lifting effect as when using other methods, for example, RF microneedle treatment.
Fractional radiotherapy with RF microneedles
Fractional radiofrequency with microneedles may be an alternative or complement to fractional laser ablation. This procedure involves simultaneous puncture (with needles) and heating of the skin (radiofrequency). Since the needles work deeper than the laser (needles up to 3. 5 mm, laser up to 1. 5 mm), we get a stronger lifting effect, often even representing an alternative to a surgical facelift because deeper layers of tissue are stimulated.
Fractional radiotherapy with RF microneedles before and after
The recovery period after radiofrequency treatment is also shorter - one day is enough for the redness of the skin to go away.
But the downside to this method is that RF microneedles do not have the same refreshing effect as an ablative laser.
The common feature of these methods is that they both work through stimulation. We deal with destruction in order to restore normal young tissue. Fractional laser has an additional peeling effect that refreshes the skin. On the other hand, RF microneedles work deeper and have a shorter recovery period.
How to apply this knowledge in practice? Both methods are equally effective against wrinkles and acne scars.
Smart face lift with threads
With age, facial skin becomes thinner and saggy, and deeper tissues are lost. Therefore, we need to stiffen the skin. In this case, smart lifting will help.
Facelift with threads before and after
Treatment consists of local injection of surgical microneedles with threads, which provide a stimulating effect. The inserted threads cause thickening and increase the density of the skin, irritating the tissue. The difference, compared to fractional laser or RF with microneedles, is that the threads create a collagen scaffold in the planned areas. Moreover, skin irritation lasts longer than in the case of a fractional laser, about 6-9 months - this is how long the threads stay in the skin before they dissolve. And the procedure itself does not require recovery - a maximum of a few hours.
L-polylactic acid
Here we also introduce a substance into the skin, the task of which is to stimulate cells to regenerate. This process takes a long time - irritation of cells with l-polylactic acid before it is completely absorbed takes several months, resulting in a gradual, clear increase in tissue volume.
L-polylactic acid before and after
This method is ideal for smoothing out tear troughs, nasolabial furrows, sunken temples or cheeks. The downside of the method is that it cannot be used in the forehead, eyelids and neck. This is where a smart facelift is ideal.
To summarize the four methods:
- Ablative fractional laser and RF microneedles are better for tightening, skin renewal, getting rid of scars and wrinkles;
- L-polylactic acid and smart lifting are better suited for increasing volume, reconstructing cavities, i. e. for volumetric treatment.
Hyaluronic acid
This method is suitable when patients want to quickly correct something, for example, nasolabial furrows. However, you should know that hyaluronic acid is only a camouflage masking the problem. Deep furrows are the result of sagging cheek skin, and the best place to start is by strengthening the tissue using laser or radiofrequency microneedling.
Hyaluronic acid before and after
When choosing a method, it is also necessary to take into account that it is not suitable for people suffering from autoimmune diseases. Although cosmetic acids are biocompatible materials, they are obtained through biotechnological processes and are not the body's own tissue, so they cause irritation to surrounding tissues. In people with autoimmune diseases, the immune system is unpredictable and overreacts to any foreign body.
Comparison of facial rejuvenation methods
| Method | How does it work | Effect | pros | Minuses |
| Ablative fractional laser | Stimulates collagen production and refreshes the skin through peeling. The time of "irritation" of the skin is thousandths of a second, and the recovery period of the skin is 1-4 months. |
Refreshing and brightening the skin, smoothing out irregularities (scars, pores), improving color, tension, increasing elasticity, increasing thickness, smoothing wrinkles. | Affects both the surface of the skin and its inner layers. Gives strong effects. |
Recovery time is up to 7 days. Gentle volumetric results. |
| Fractional RF microneedles | Stimulation by mechanical and thermal effects. The time of "irritation" of the skin is tenths of a second, and the recovery period of the skin is 1-4 months. |
Strong lifting effect, smoothing out irregularities (scars, pores), tightening, increasing elasticity, increasing thickness, smoothing wrinkles. | Recovery time: 1 day. Strong effects | Does not refresh the surface of the skin - no peeling of the skin. |
| Volume restoration | Stimulation through irritation (surgical microsections). Skin "irritation" time: 6-9 months. |
Restoring skin volume, increasing its thickness and elasticity, restoring cavities where necessary, lifting effect. | Recovery time: several hours. | Does not refresh the skin surface (no skin peeling) The risk of an overactive reaction of the body. |
| L-polylactic acid | Stimulation through irritation (l-polylactic acid). Skin "irritation" time: 9-12 months. |
Restoring skin volume, increasing its thickness and restoring cavities where necessary, a lifting effect. | Recovery time: 1 day (but there is a risk of bruising). | The risk of an overactive reaction of the body. Cannot be used on all areas (eg neck, forehead). |
| Hyaluronic acid | Eliminates wrinkles, furrows and cavities by filling them. Skin irritation time: no. | Elimination of wrinkles and furrows by filling them. Changing the shape of the face by increasing the volume of highlighted parts or filling in gaps. | Quick effect. Recovery time: 1 day (risk of bruising). The ability to dissolve acid in case of improper (ugly) treatment. |
The effect is due to the administration of the drug, and not to tissue regeneration. Relatively short duration of action. Possibility of moving the drug. |